Welcome to my ultimate guide to Ethereum Staking where I’ll tell you everything you need to know about staking on Ethereum. You’ll get an overview of what staking is and all the different methods through which you can do it. It’s important that you listen carefully until the end of the video because each staking method has its own respective requirements that, depending on things like your budget, risk tolerance or the number of ETH you hold, will make some methods more suitable for you than others.
Proof of Stake
Ethereum’s proof-of-stake consensus mechanism relies of stakers to validate and produce new blocks. To start staking, a user is required to deposit ETH into the staking smart contract and run software that helps check and create new blocks propagated to the network. When you run this software on a computer, it becomes what is known as a validator node. In return for providing this service, adding to the decentralization and security of the Ethereum network, you will earn rewards in the form of ETH which amount to just under 5% APR. Its passive income that’s risk free, so long as your node does not behave improperly and try to cheat the system in some way. In that case, you would experience a slashing penalty that takes a percentage of the ETH you deposited into the staking smart contract.
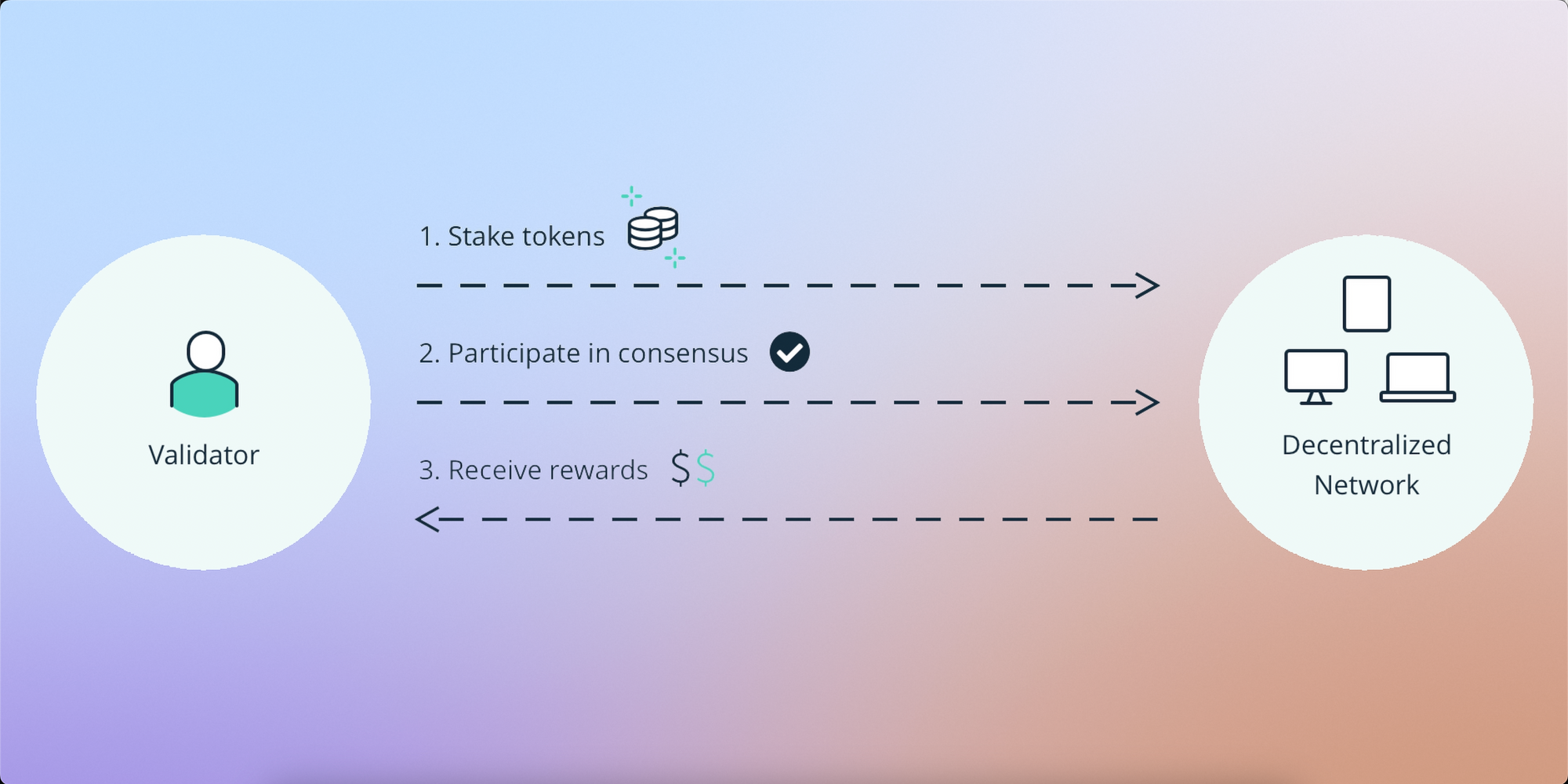
Now, let’s go over the various staking methods in order from most ideal to least ideal. But first, a message from this video’s sponsor, Stader.
Stader is a leading multi-chain liquid staking platform that has just expanded to Ethereum with the launch of ETHx. Designed to keep Ethereum decentralized by providing an accessible, reliable, and rewarding liquid staking solution, ETHx allows anyone to start running a validator node with only 4 ETH per validator. To celebrate the launch of ETHx Stader has partnered with Allnodes where you can easily spin up ETHx nodes for $5 a month. There’s a 1 year 40% commission boost for the first 4 validators set up per operator during the launch month. Join the Stader discord community for 24/7 support and to find out more. Link in description.
Solo Staking
Getting back to the video, the first and most ideal staking method is known as Solo Staking. It’s where you set up and maintain your own Ethereum validator node and deposit 32 ETH into the staking smart contract. The main benefit being that you have full control over your keys that enable withdrawing or transferring staked funds. You don’t need to trust a 3rd party with your ETH. In doing so you earn the full staking reward as there is no need to pay any service fees. By running your own validator node, you are also contributing to the decentralization and security of the Ethereum network.

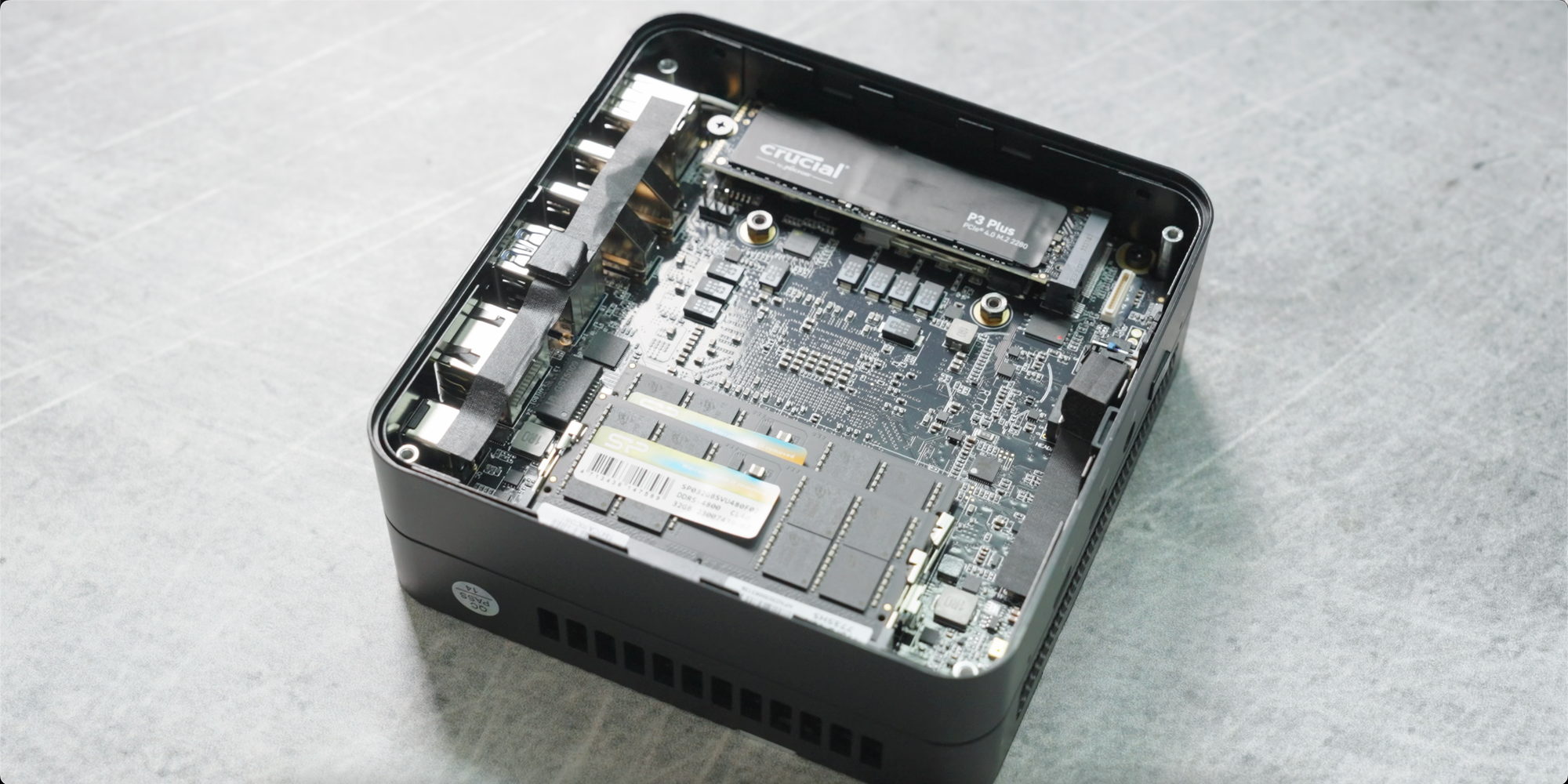
Solo staking is how Ethereum staking was intended to be done, but there are several hurdles involved. The first being that the required 32 ETH is a lot of money, $60,000 at the time of filming, and that will eliminate this staking method for many people. Additional requirements include the need to purchase, set up and maintain your validator node hardware. You could easily spend $1000 dollars buying a suitable mini-pc to run your Ethereum node and then you need to configure it which requires a certain degree of technical competency. If that is too difficult for you there are some providers of pre-configured node hardware that are plug and play, although their pricing is heavily inflated. Once your validator node is operational, it will require a stable internet connection that can handle upwards of 1.5 Terrabytes of internet usage per month, according to Ethereum.org, so ideally you’d want to be on an unlimited high bandwidth internet plan. Moreover, if for whatever reason your validator node goes offline you may incur some reward penalties. It’s important to ensure your node maintains a high level of uptime. If you have 32 ETH I highly recommend choosing this staking method. To make things easier for you, I’ve gone through the effort of creating a step-by-step tutorial for setting up an Ethereum validator node and you’ll find it up here when I publish the video.

Staking as a Service
However if this sounds too daunting and you still have 32 ETH, there is an alternative staking option called Staking as a Service (SaaS) which may be the right fit for you. With Staking as a Service, you are delegating everything to do with the validator node operation to a third party. This means there’s no need to purchase hardware, no complicated setup, and no ongoing maintenance. It’s even possible to maintain control over your keys for withdrawals. In exchange for providing this service, Staking as a Service providers do take a monthly fee and thus you would not be earning the maximum possible APR.

For some, paying a monthly fee for a quick and easy staking solution is preferred to investing in the hardware and going through the tedious setup required to solo stake. When looking for a provider there are some key factors that you need to consider, such as whether their code is open source and if they have undergone an audit. If a provider hasn’t done this, then by choosing them you would be introducing a level of trust and risk that could easily be avoided. Make sure to do your own research and choose wisely.
Pooled Staking
The methods of staking which I’ll cover next are for all of you who hold less than 32 ETH, starting with Pooled Staking. Like mining pools, where users pool their computing resources together, staking pools allows users to combine their ETH and have enough to collectively run a node. You can do Pooled Staking in two different ways, first where you are Staking Pool Node Operator or second where you are simply a participant in the pool which can be referred to as Liquid Staking. If you have hardware suitable for solo staking, see my solo staking tutorial to find out, you’ll want to be a pool node operator as it comes with additional benefits. Rocketpool is one of the popular pooled staking platforms that offers this, and you only need to deposit 8 ETH + 2.4 ETH of RPL tokens to create what they call a minipool. The balance to make up 32 ETH comes from other users and then you have a validator. Pool node operators, in addition to their respective portion of the validators ETH rewards, receive commission from the other participants that brings the reward to about 10% more than if you were solo staking. It’s also possible to run multiple minipools on a single node device to maximize your profits. These extra rewards are only guaranteed if your node performs smoothly. If there are issues with your node’s performance that result in the minipool losing funds, then ETH is taken from your share of the pool.

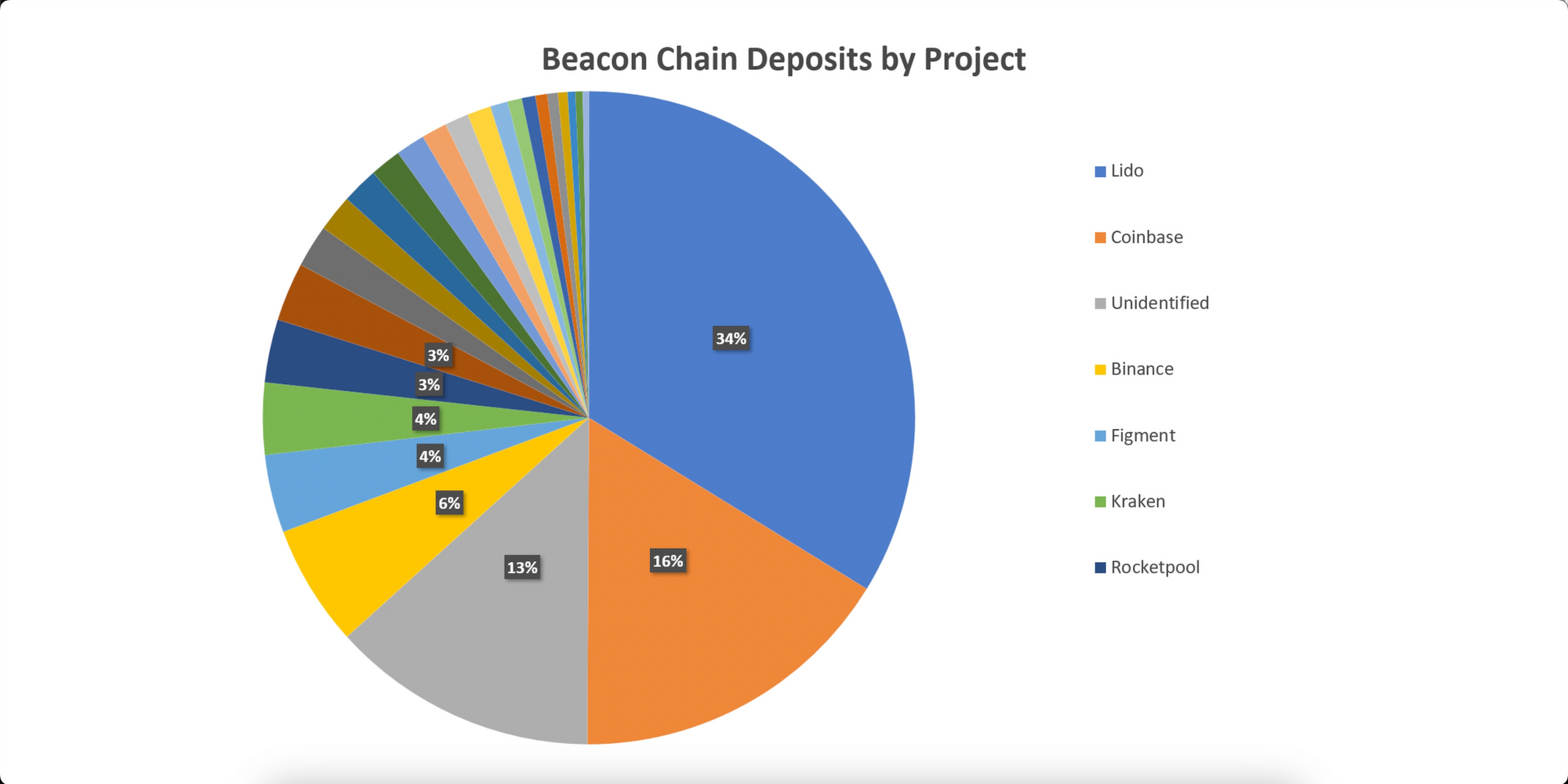
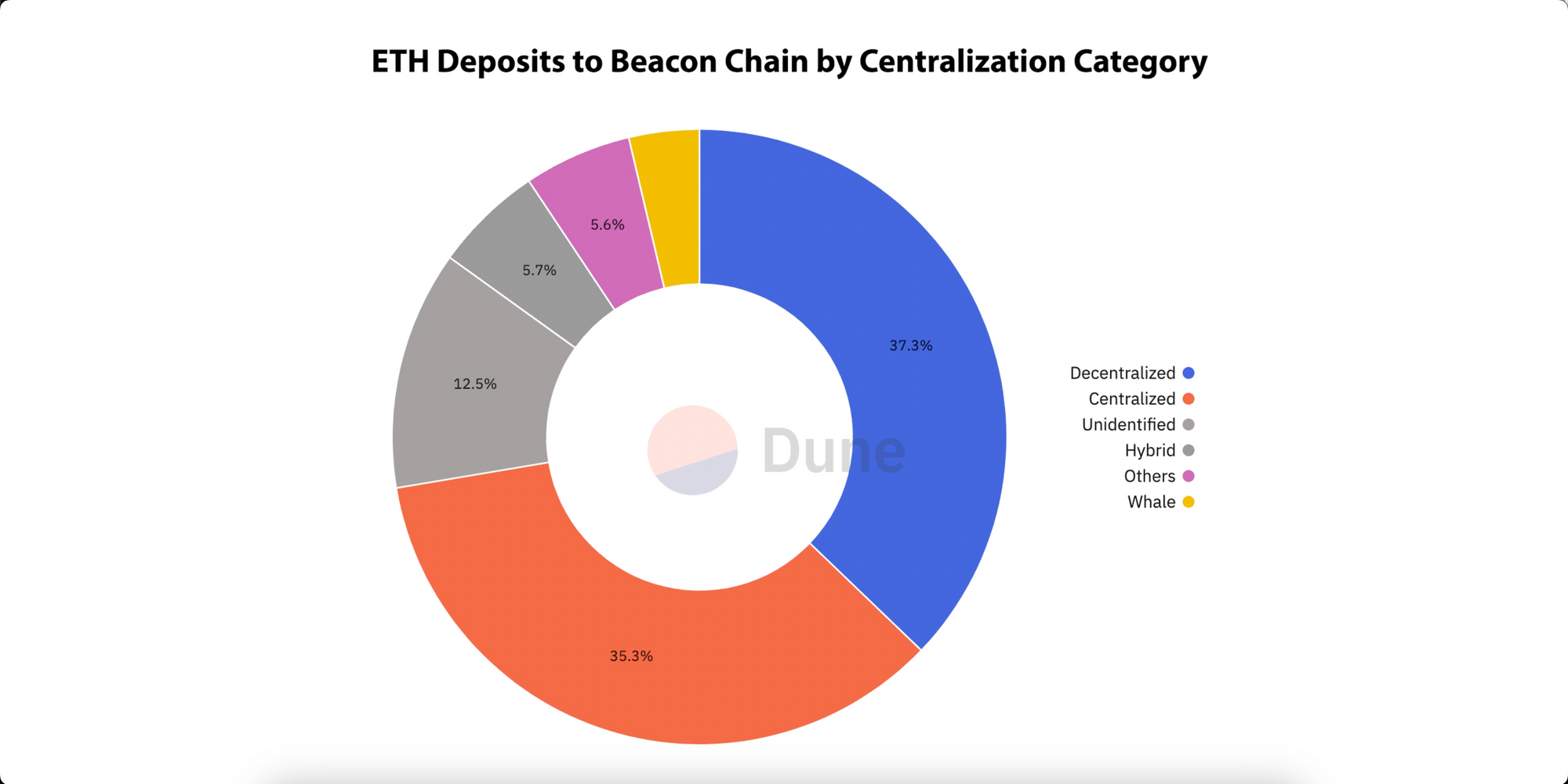
On the other hand, if you are merely a participant in the pool, you don’t have to worry about any of this. You can contribute any amount of ETH and start enjoying the benefits of staking by simply performing a token swap. Staking pools all have something called a Liquid Staking Token that represents a share of the ETH staked in a pool. If you buy an amount of these tokens and hold them, you are staking. The value of the tokens increases every day relative to ETH as staking rewards accumulate. So when you go to sell them at a later date, you will receive more ETH than what you bought the liquid staking tokens for. Any profit is minus the commission you pay, which in the case of Rocketpool is 15%. So while liquid staking offers the fastest and easiest way to participate in Ethereum staking, the rewards are not as high and you are also trusting that the provider will honor the redemption of the tokens for ETH. Another downside is that it doesn’t help keep the network decentralized and we’ve already seen one liquid staking provider, Lido, grow to the point where it accounts for over 30% of Ethereum validator nodes. This poses the risk that an entity of this size could act maliciously and cause damage to Ethereum, or they may be subject to sanctions and regulatory overreach by governments as we have seen more of in recent times.
Staking on Centralized Exchanges
This brings us to the final staking method, which is done through Centralized Exchanges. This requires the least amount of effort as it can be done in a few clicks and the exchange handles all the hard work, but it is not at all recommended for reasons which we will now get into.

First and foremost, you’ve probably heard the saying “not your keys, not your coins”. By storing your ETH in an exchange, you are relinquishing control of your coins to them and if they blow up for whatever reason then your money is gone. We’ve seen this time and time again, with platforms as old as Mount Gox or as recently as FTX which certainly won’t be the last. Centralized exchanges also control a large amount of nodes which does not contribute toward keeping Ethereum decentralized. Further, centralized exchanges have been targeted by the SEC in the United States for offering these staking services, which the SEC says are unregistered securities. They’ve been going after the biggest players like Coinbase, Binance and Kraken, suing them and giving them 10’s of millions of dollars in fines. The battle in that arena is far from over and there is simply no good reason to throw your money on any of these platforms and put it at risk.
Final Thoughts
That’s it, that was everything you guys need to know about staking on Ethereum. If you found this video helpful, please leave a thumbs up or comment and share it with your friends. It won’t be the last video I make on this topic either, as I have several other detailed guides in the pipeline. Subscribe now so you don’t miss out, and I look forward to seeing you again in the next one.




