In this video you’re going to learn all about Ethereum’s next big upgrade which is set to go live by the end of Q1 2023. The upgrade, known as Shanghai, implements several Ethereum Improvement Proposals that will have significant implications on the network, including the ability to withdraw staked Ethereum. People have been staking their Ethereum since the launch of the Beacon chain in December 2020 and there is currently around 16 million ETH locked, equivalent to 22 billion dollars. With over 13% of the Ethereum supply suddenly becoming liquid, many people are convinced that Shanghai will trigger a devastating selloff in the markets that sends Ethereum to new lows. Personally, I completely disagree with these theories. To find out why, make sure you stay tuned till the end of the video.

Let’s begin by understanding where Shanghai fits in to the larger Ethereum scaling roadmap of which there are 3 major milestones. The first was the launch of the Beacon Chain, the proof of stake blockchain that introduced staking. Then there was The Merge, which saw the original proof of work mainnet join with the Beacon Chain to become a single chain. Finally there is Sharding, which aims to improve scaling and capacity for storing data when it ships in late 2023 or in 2024. In-between these there are several additional upgrades, and that’s where Shanghai comes in. The Ethereum community uses a process called Ethereum Improvement Proposal, also known as EIPs, to propose potential changes to Ethereum. An EIP must go through several stages of discussion, design, and implementation by Ethereum Developers and the community before it can be chosen for inclusion in an upgrade.
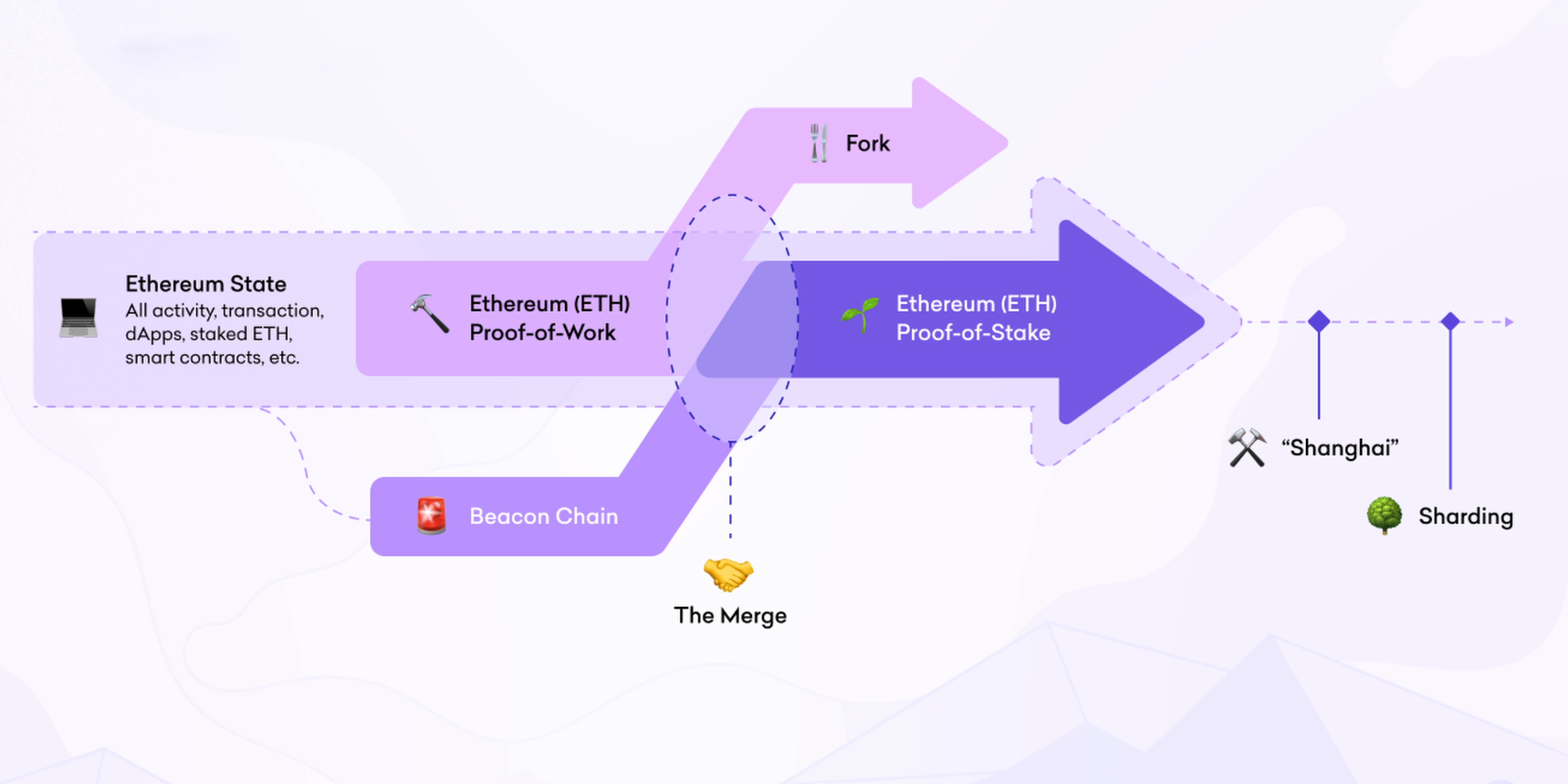
Shanghai, whose testnet is expected to go live in February before the mainnet launch in March, will include 4 EIPs which we’ll now take a closer look at. EIP 3651, Warm COINBASE, changes the COINBASE from cold to warm which significantly reduce the gas fees paid for direct coinbase payments. This benefits block builders, who ultimately pay less fees. EIP 3855, PUSH0 Instruction, adds a new smart contract instruction to push the constant value 0 onto the stack. Not only does this reduce the size of the smart contract, but it also reduces the gas required for deployment. EIP 3860, Limit and Meter Initcode. The initcode is executed during the contract deployment process and its size will now be limited to 49152 bytes, which is double the code limit. The addition of gas fee metering will ensure that fees are fairly charged and also proportionate to the smart contract size. Finally, there is the most significant EIP of them all, 4895, Beacon Chain Push Withdrawals As Operations. This enables validators to withdraw their staked Ethereum, and any rewards they have generated, without incurring any gas fee.
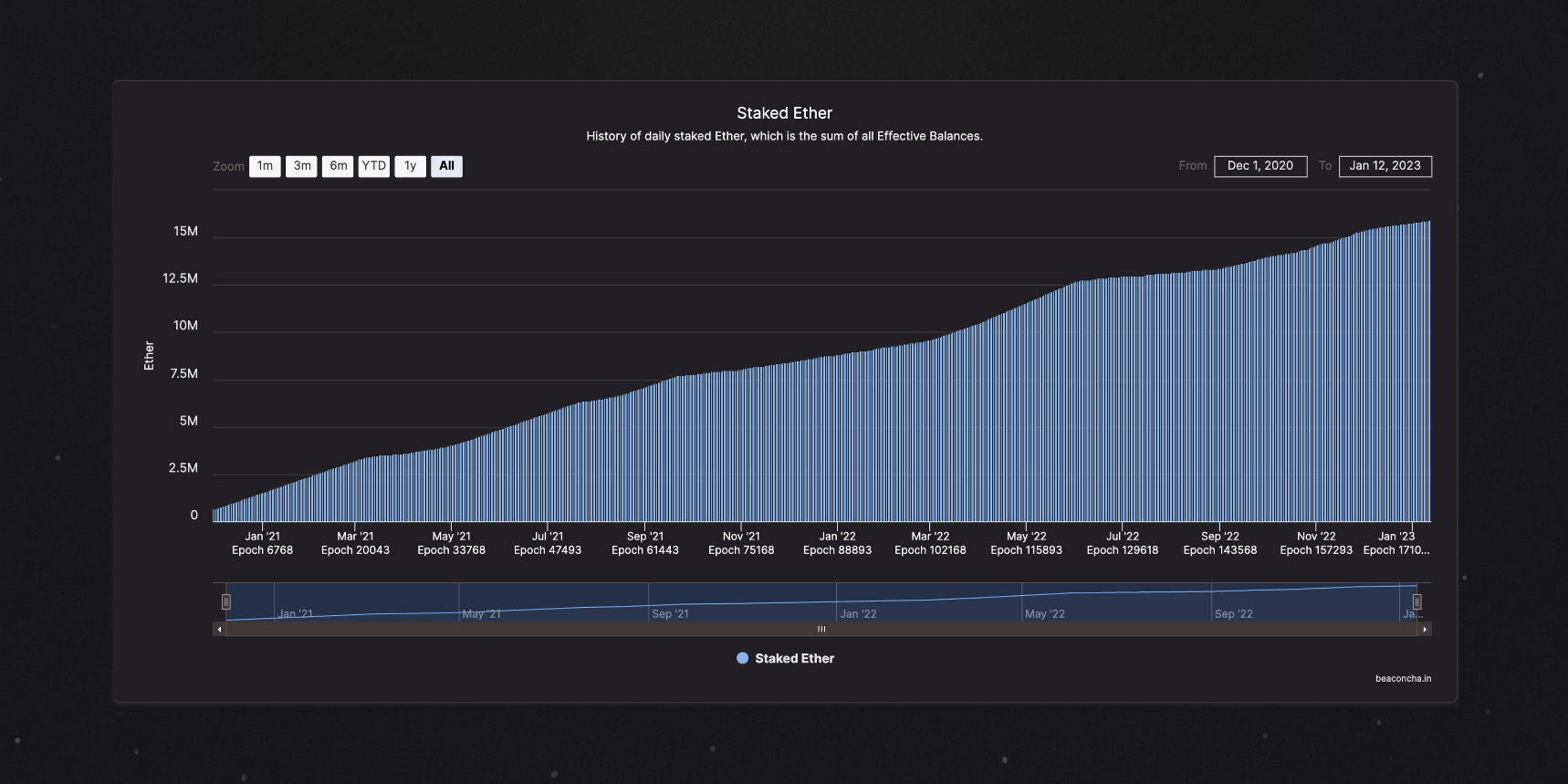
This doesn’t mean however, that when EIP 4895 is implemented the validators will unstake and then proceed to sell their coins. That is pure FUD in my opinion. In addition to earning passive income, part of the reason people stake their Ethereum is because they believe in the long-term future of the project. This is especially true of the current group of validators, as they knowingly staked their coins with no ability to withdraw. Some went even further by staking their coins before the merge, when there weren’t any staking rewards. My prediction for the Shanghai upgrade is that once the withdraw functionality is implemented, we’re going to see a huge influx of users wanting to stake their Ethereum and become validators. This is because Shanghai will have eliminated most of the risk associated with this activity. Companies, DAOs and other entities which hold ETH will likely all begin to take advantage of staking to earn interest and grow their stack. All of this means less Ethereum on the open market and that will ultimately have a positive effect on price.
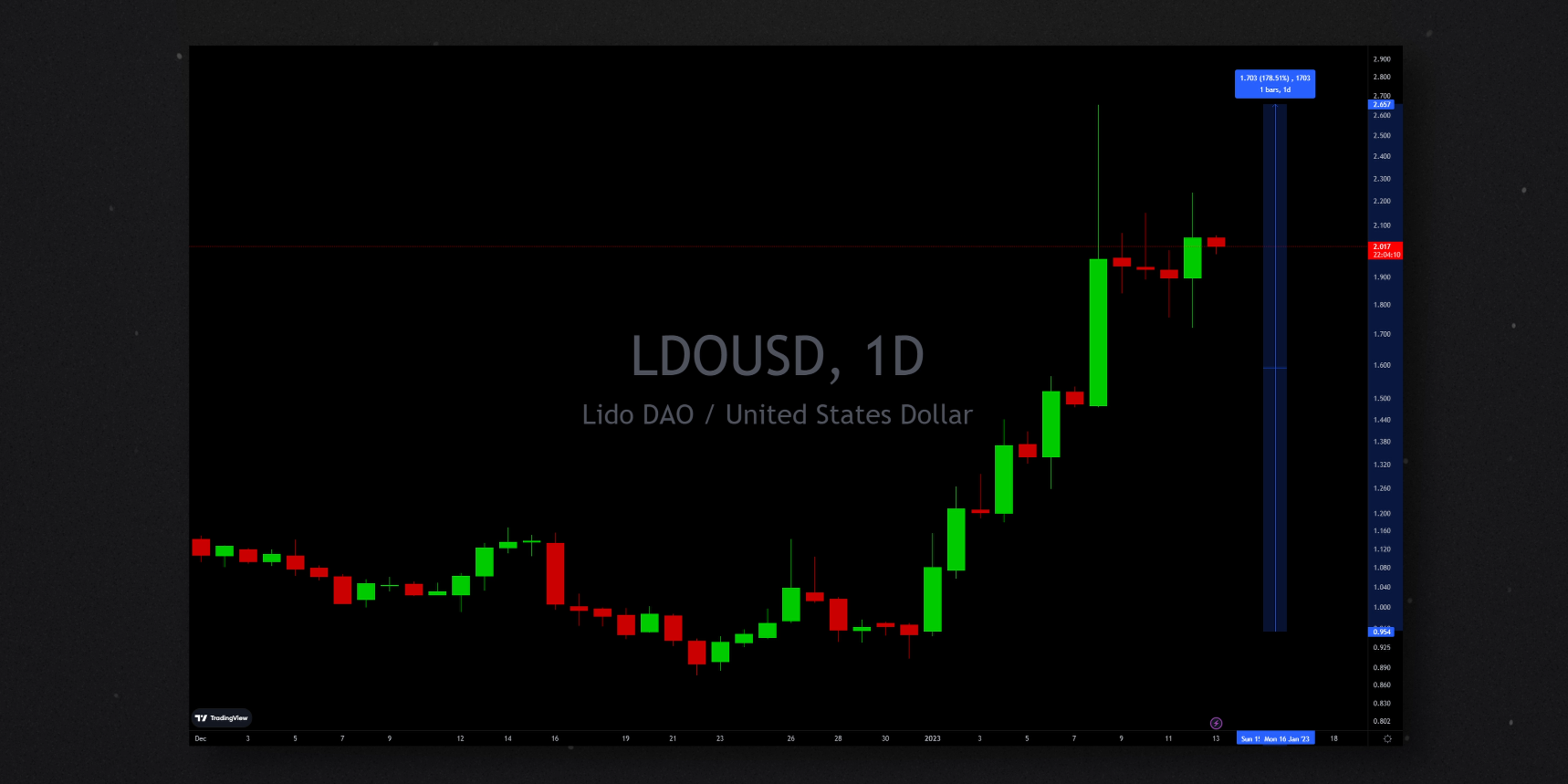
Just this week, in anticipation of the Shanghai upgrade, we have seen huge pumps on tokens associated with liquid staking protocols. These solutions, of which major players include Lido Finance and Rocket Pool, allow users enjoy the benefits of staking without putting up the required 32 ETH to become a validator. You can give them any lesser amount and they will stake it for you, jointly with the funds of other customers. It basically works in a similar fashion to a mining pool. Since January 1st, the governance token of Lido Finance pumped by as much as 180% while Rocket Pool’s rose about 50%, showing a great deal of confidence in these protocols in the leadup to Shanghai.
So, what comes next? Well following Shanghai the next upgrade will be called Cancun. Ethereum developers will shift their focus toward EIP 4844, also known as Proto-Danksharing. This update is arguably of greater importance than Shanghai, as it will greatly benefit Ethereum scaling. 4844 will increase transaction throughput and cut down on absurdly high gas fees, while also laying the groundwork for full Sharding later down the track. For anyone interested in this technology, its crucial that you stay informed on developments like these and the best way to do that is by subscribing to this channel. So go ahead now and click the subscribe button. Also if this video helped you better understand the Shanghai upgrade, give me a like and share the video with your friends. I hope to see you all on the channel again next time, peace.




